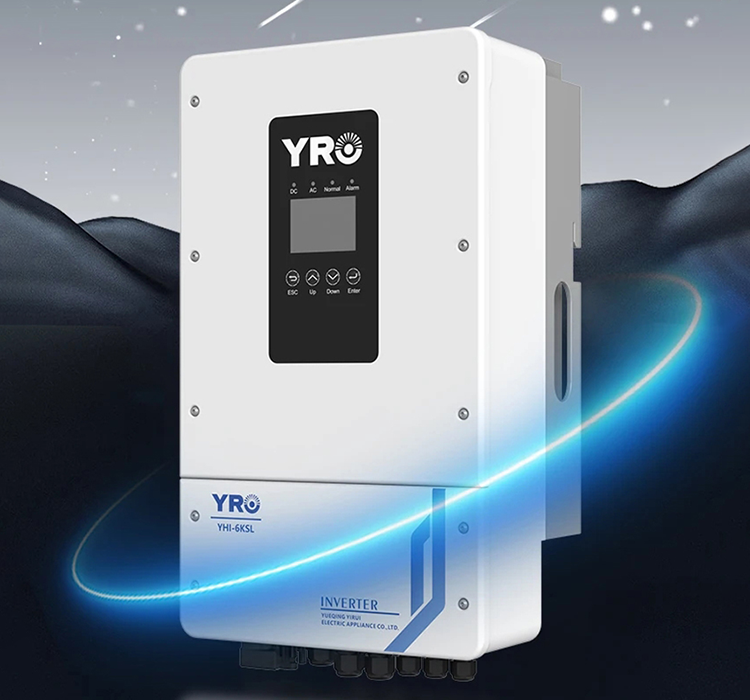
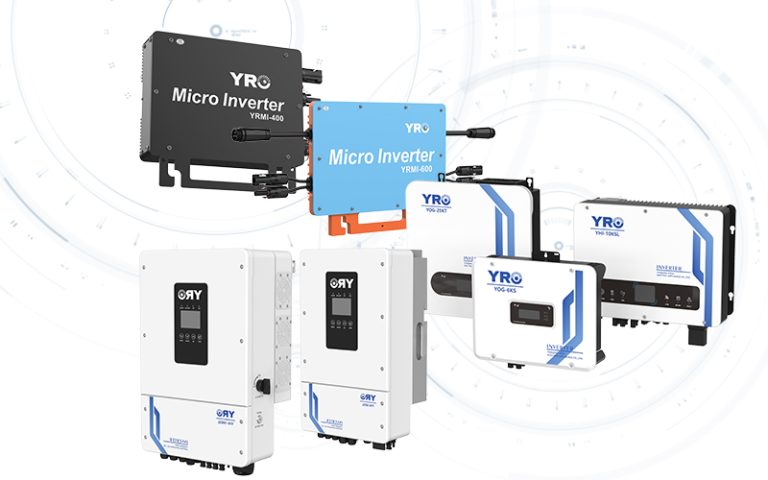
An on-grid, off-grid, hybrid inverter is a sophisticated piece of technology used in solar photovoltaic (PV) systems. It combines the functionalities of both on-grid (grid-tied) and off-grid inverters, allowing a solar PV system to operate with versatility in various modes.
On-Grid Inverter:
Grid-Tied Operation: In this mode, the inverter allows the solar PV system to be connected to the utility grid. It converts the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power compatible with the grid.
Net Metering: When the solar system produces more electricity than is consumed, the excess can be fed back into the grid, often with credits received through a net metering arrangement.
Grid Dependency: On-grid systems typically do not provide power during a grid outage as they are designed to shut down for safety reasons (anti-islanding).
Off-Grid Inverter:
Independent Operation: Off-grid inverters enable the solar system to operate independently of the utility grid. They are often used in remote locations where grid power is not available.
Battery Storage: They require battery storage to store excess solar power for use when the solar panels are not producing electricity, like during the night or on cloudy days.
Power Management: Off-grid inverters are responsible for managing the energy flow from the solar panels to the loads and the battery, ensuring the system’s reliability.
Hybrid Inverter:
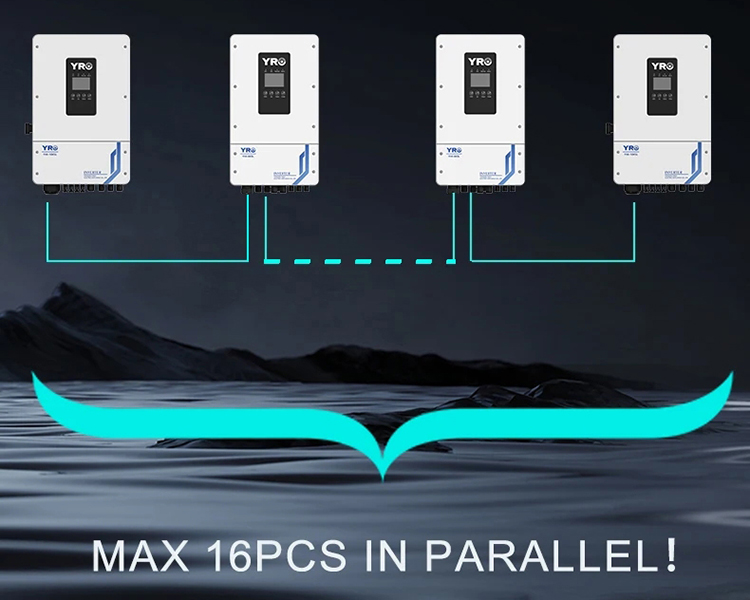
Combination of On-Grid and Off-Grid: Hybrid inverters combine the features of both on-grid and off-grid inverters. They can feed power into the grid, store energy in batteries, and provide power to the home or business independently of the grid.
Energy Storage: Like off-grid systems, hybrid inverters are used with battery storage. This allows for energy to be stored when production exceeds consumption and used when needed.
Grid Outage Support: One of the key advantages of a hybrid system is its ability to provide power during a grid outage by switching to off-grid mode and using the stored battery power.
Smart Energy Management: Many hybrid inverters come with intelligent management systems that optimize energy use, deciding when to store energy, when to use it directly, and when to sell it back to the grid.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency: By allowing for both grid interaction and independent operation, hybrid systems can be more cost-effective and efficient, maximizing the use of solar power and reducing reliance on the grid.

Applications:
Homes and Businesses: Ideal for locations where grid power is available but unreliable, allowing for continuous power supply even during outages.Remote Locations: Useful for off-grid installations where grid power is not an option but where occasional grid interaction may be desired.