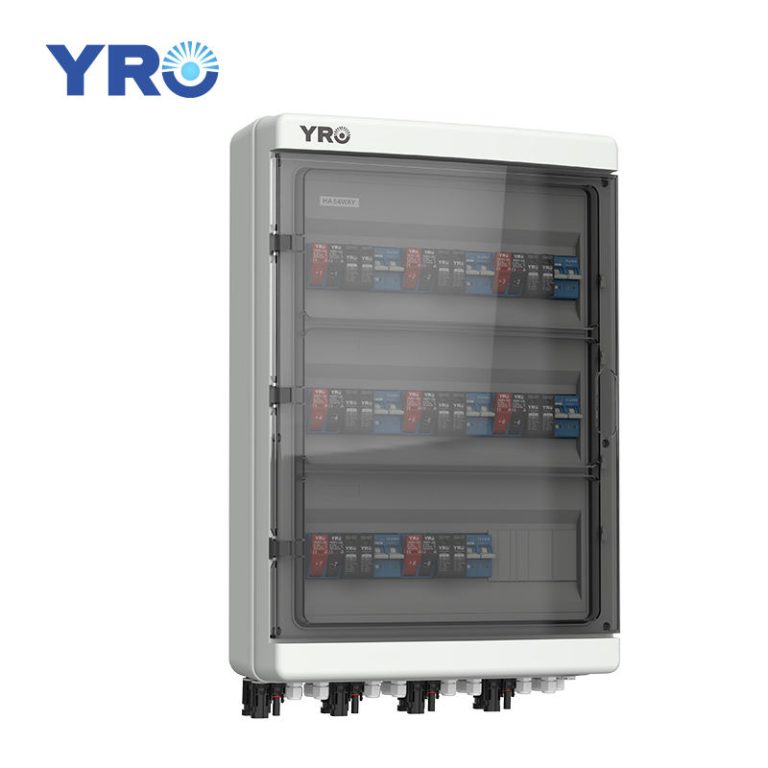
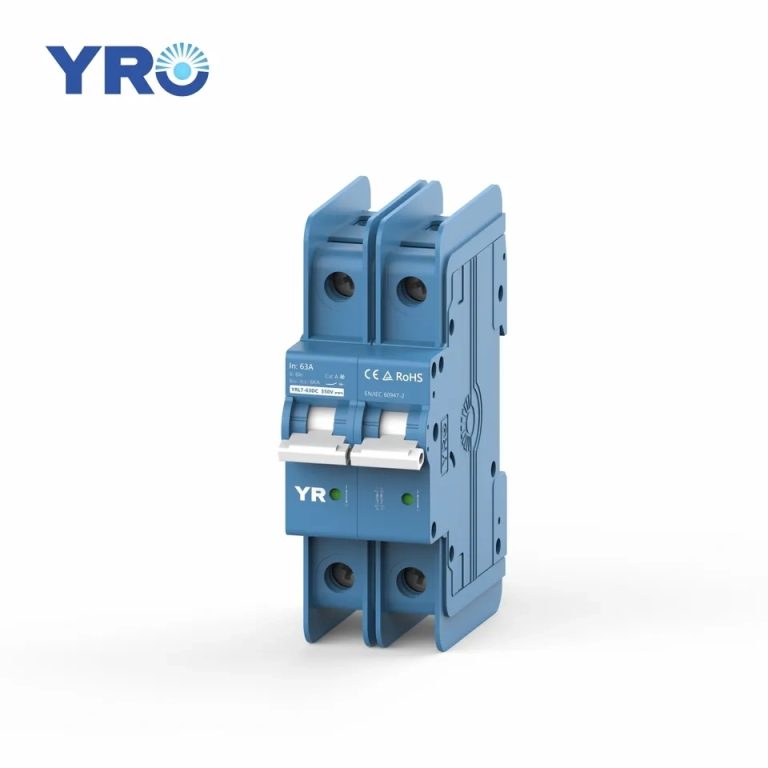
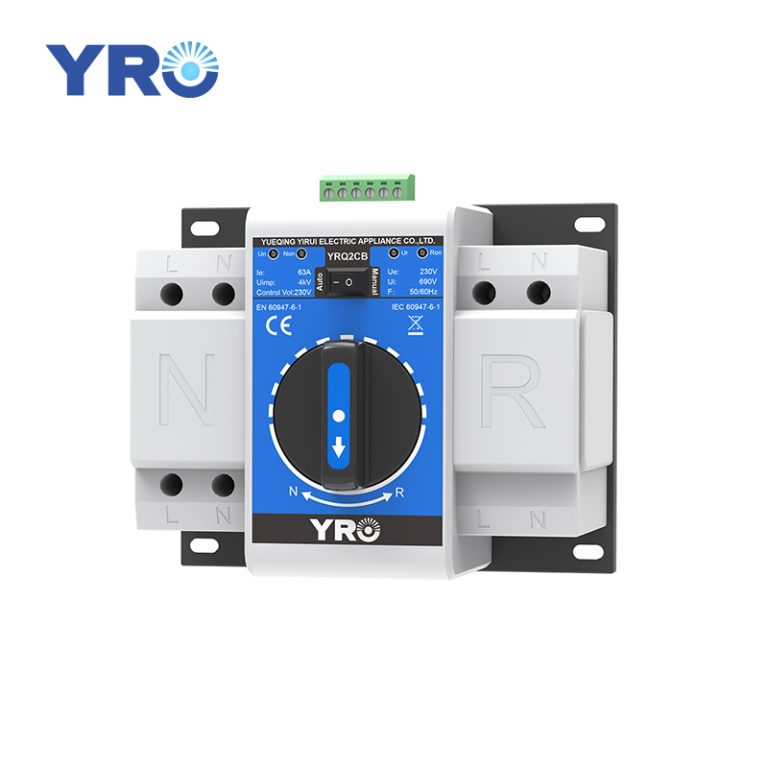
A circuit breaker is an automatic switching device used to protect an electrical circuit. Its main function is to automatically cut off the circuit in the event of an overload (i.e., the current exceeds a safe value), a short circuit (i.e., there is a low-impedance path in the circuit that causes the current to rise dramatically), or a ground fault (i.e., the current flows to an unintended path, such as a ground) in the circuit, preventing damage to the wires and electrical equipment due to overheating, or even causing a fire.
Ⅰ. what is a molded case circuit breaker?
A Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB), also known as a device circuit breaker, is an electrical protection device used to protect circuits from faults such as overloads and short circuits. Its case is usually made of an insulating material such as plastic, hence the name “molded case” circuit breaker. Moulded case circuit breakers are equipped with both thermal magnetic and electronic overcurrent arresters, which can provide different protection functions according to different application scenarios
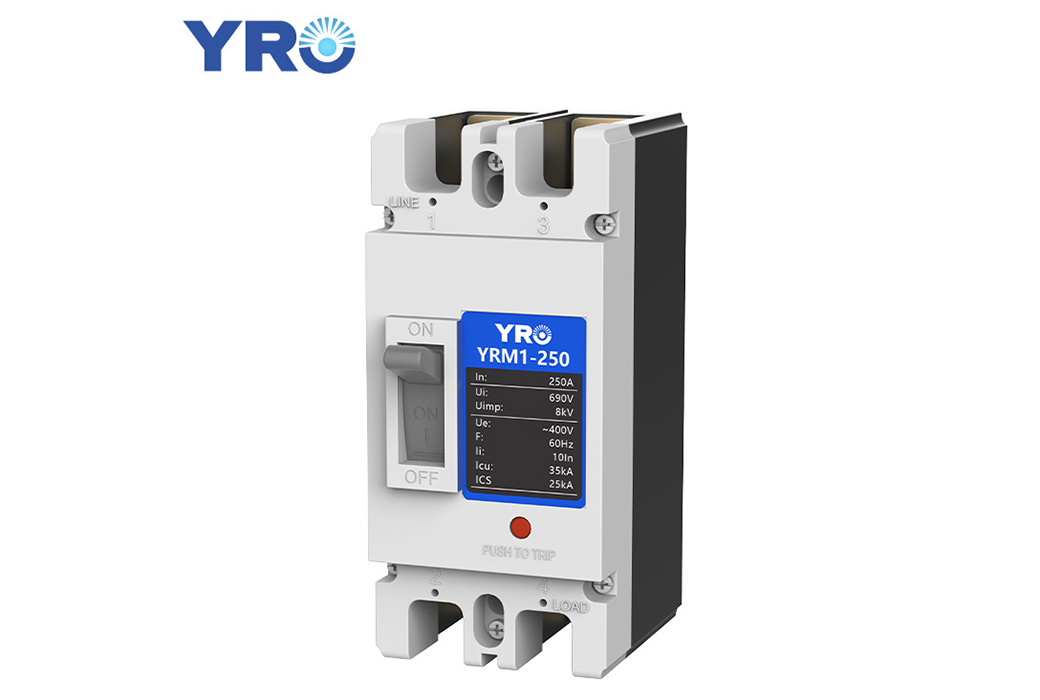

Ⅱ. What Does a Standard Molded Case Circuit Breaker Contain?
To fully understand the function of an MCCB, it is important to understand its different components and how they work together; an MCCB consists of a number of key components, each of which has a specific purpose.
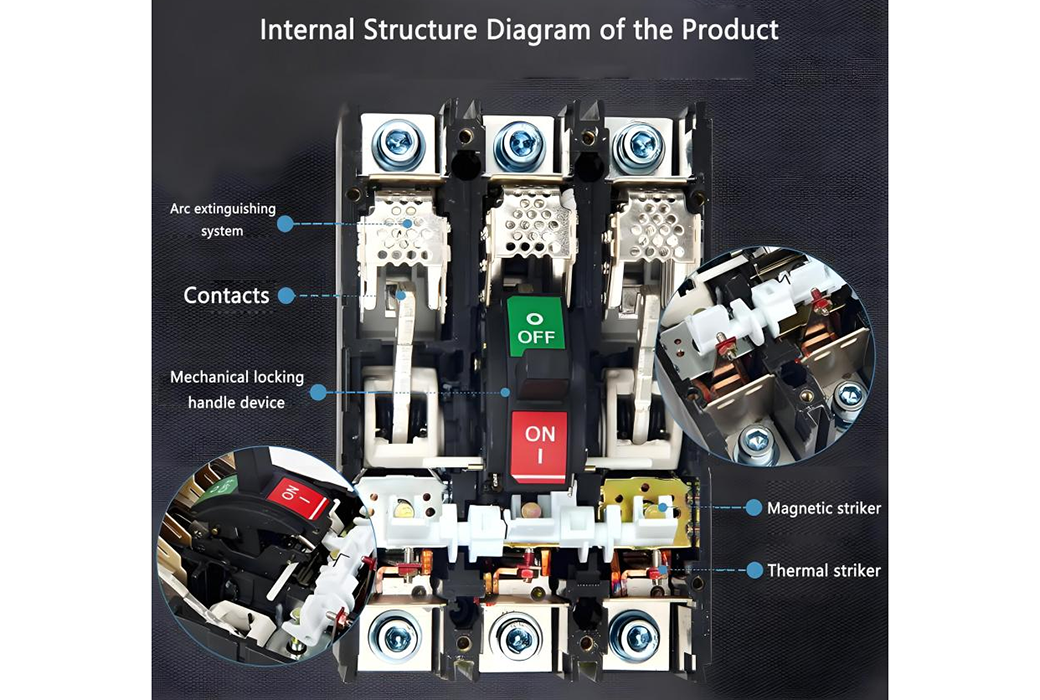
1. Enclosure: made of high temperature and impact resistant insulating plastic material, such as polypropylene (PP) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which protects the internal structure from the external environment and provides insulation
2、Contacts: used to connect and disconnect the circuit, including fixed contacts and moving contacts.
3、Stripping mechanism: including thermal striker and magnetic striker
– Thermal striker: detects the overload current in the circuit and breaks the circuit by bimetal bending with heat to prevent overheating and equipment damage. With delayed action characteristics, it can distinguish between short-term current surges and continuous overloads.
– Magnetic striker: detects the short-circuit current in the circuit, and quickly cuts off the circuit through the strong magnetic field generated by the electromagnetic coil. Rapid response, able to act in the short-circuit instant, to protect the circuit and equipment
4、Operating Mechanism: Provide manual and automatic operating functions for the opening and closing operation of the circuit breaker.
5、Arc extinguishing system: used to extinguish the arc that may be generated when the circuit breaker breaks the circuit to protect the contacts from damage.
6、Status Indicator: It displays the current status of the circuit breaker (e.g. “open”, “closed” or “fault”), which is convenient for users to monitor and manage. Generally mechanical indication or LED light display.
7、Connection terminal: used for connecting in and out of the cable or wire.
8, auxiliary contacts (optional): to provide remote monitoring and control functions, can be connected with other equipment or systems to achieve linkage control.
Through the synergy of these core components, MCCB can efficiently and reliably protect the electrical system from overloads and short circuits, ensuring the safety of electrical equipment and personnel.
Ⅲ. What Is the Difference Between MCCB and MCB?
Moulded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) and Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) are both important devices used to protect electrical systems, and although they work very similarly, there are some differences.
|
Point of Difference
|
MCB
|
MCCB
|
|
Full Form
|
Miniature Circuit Breaker
|
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker
|
|
Definition
|
An automatic electrical switch designed to protect low-voltage circuits and appliances from overcurrent and short circuits
|
A circuit breaker that protects higher current circuits from electrical overloads and short circuits
|
|
Current Rating
|
Usually up to 125A
|
Typically ranges from 16A to 1600A
|
|
Short Circuit Time
|
Faster turn-around time (milliseconds)
|
Slower turn-around time (milliseconds to seconds)
|
|
Short Circuit Current Rating
|
Lower short circuit current ratings, up to 15kA
|
Higher short circuit current ratings, often up to 100kA
|
|
Remote Operation
|
Usually not equipped with remote operation capabilities
|
May have remote operation options for opening and closing the circuit breaker
|
|
Interrupting Current Rating
|
Lower interrupting capacity compared to MCCBs, often up to 1800A.
|
Higher interrupting capacity, suitable for more demanding applications, often going up to 200kA.
|
|
Number of Poles
|
Usually 1, 2, or 3-poles
|
Typically 3-poles (some models may have 4-poles)
|
|
Trip Circuit
|
Fixed tripping circuits
|
Movable tripping circuits
|
|
Trip Characteristics
|
Fixed, non-adjustable trip characteristics, generally suitable for general-purpose applications
|
Adjustable or fixed trip characteristics, suitable for various applications and coordination needs
|
|
Protective Function
|
Provides overload protection, short circuit protection and ground fault protection,with adjustable protection settings for greater flexibility.
|
Provides basic overload and short-circuit protection,usually have fixed protection settings and are less adaptable.
|
|
Price
|
Simple construction and relatively low price
|
Typically more expensive due to more complex construction and more protection functions provided.
|
|
Applications
|
Residences, offices, small commercial establishments, and light industrial applications with lower current requirements.
|
Factories, data centers, large buildings, and heavy-duty applications requiring higher rated current and stronger protection capabilities.
|
In general, MCCBs are circuit breakers designed for electric motors and higher power applications, while MCBs are for lower power and smaller circuits. Hopefully the differences listed above will help you understand which one best meets your requirements. Be sure to purchase from an authorized source such as Experian Electric. Visit our Yirui Electric online store for a complete range of products.