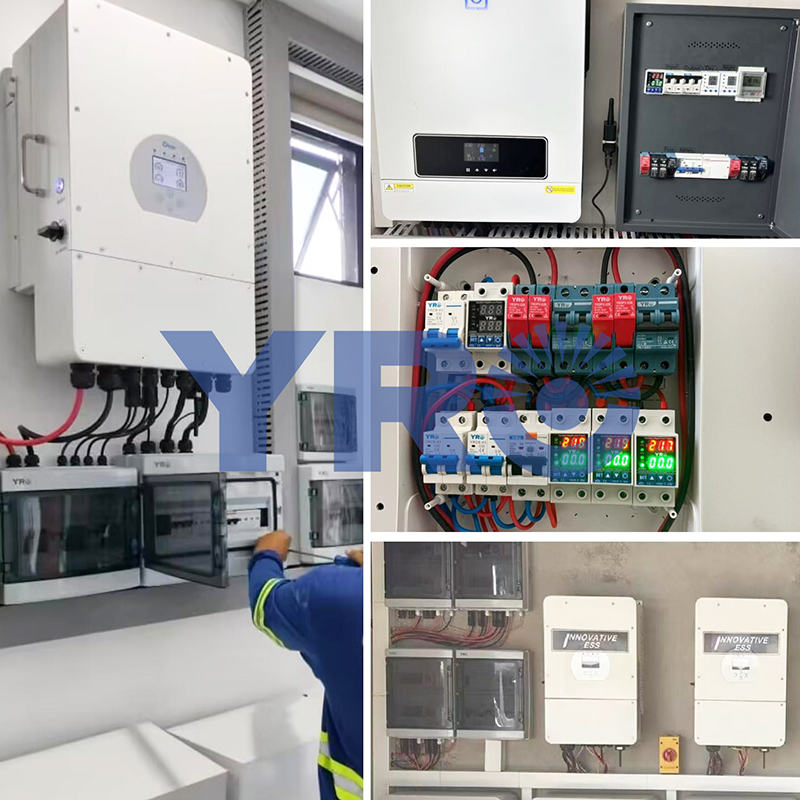
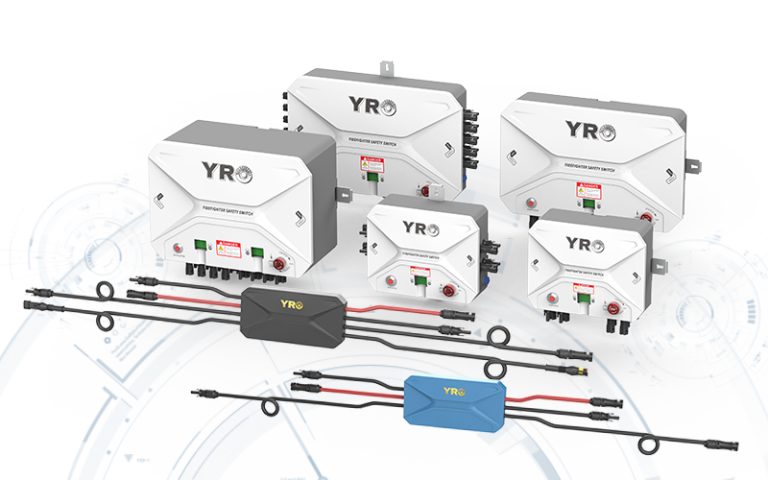
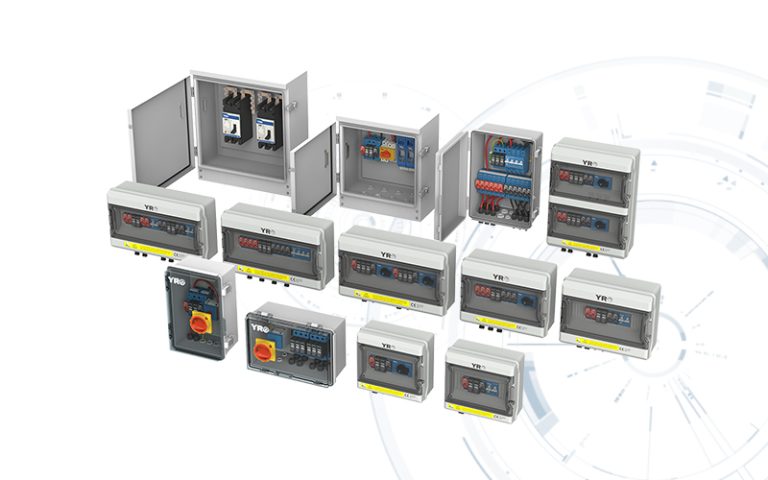
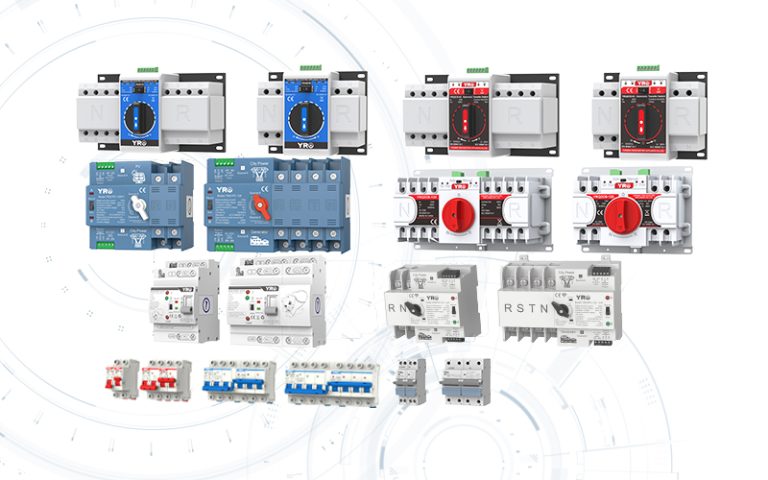
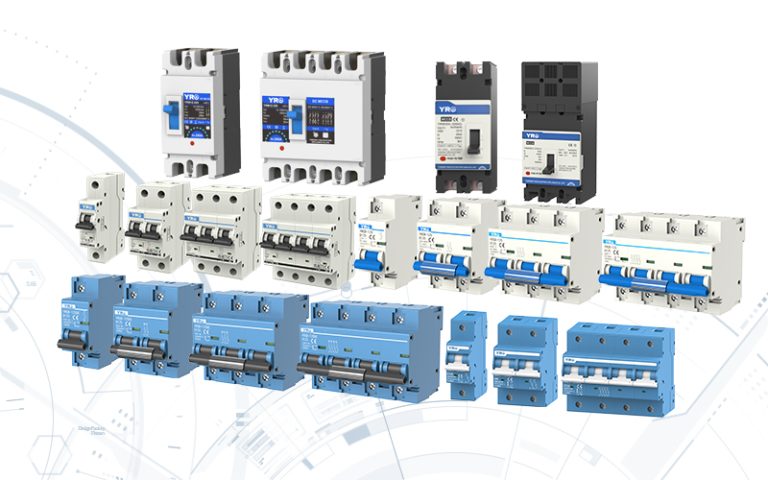
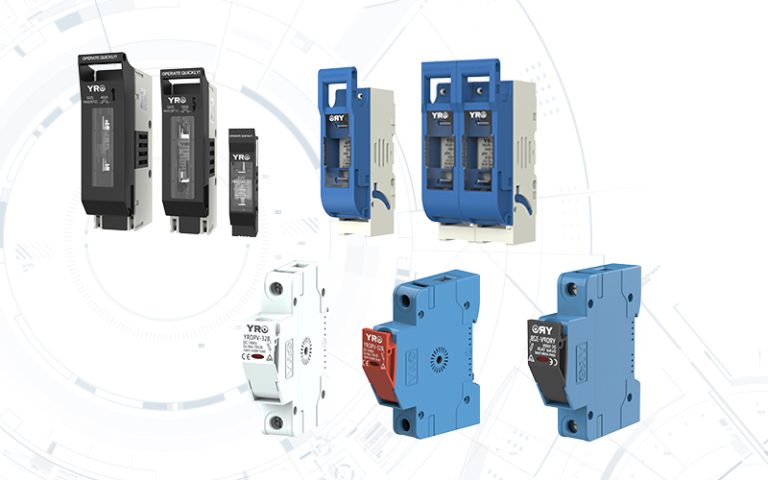
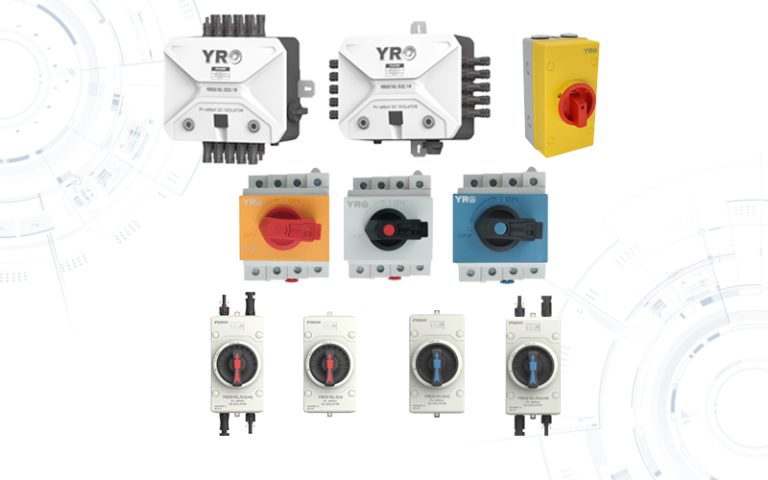
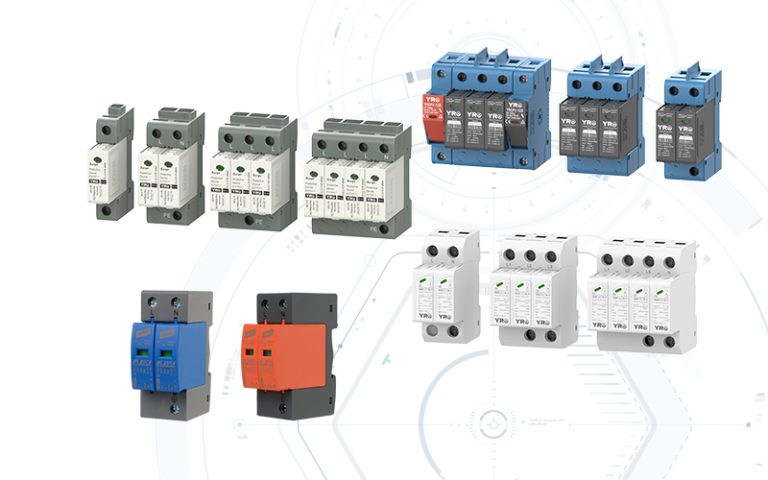
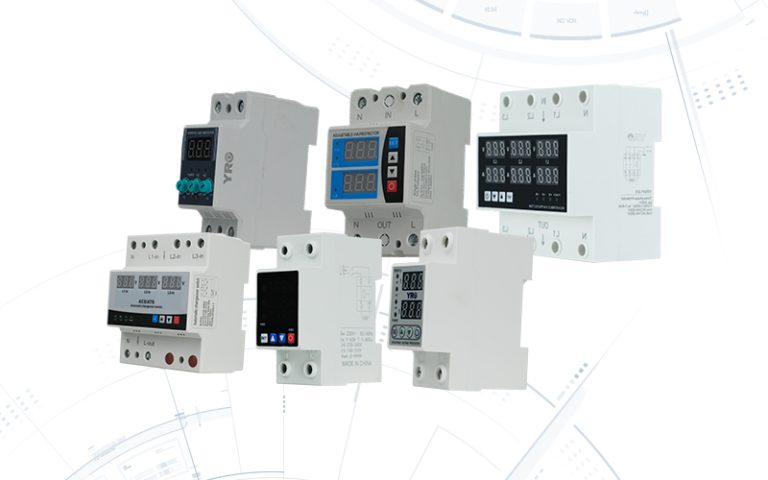
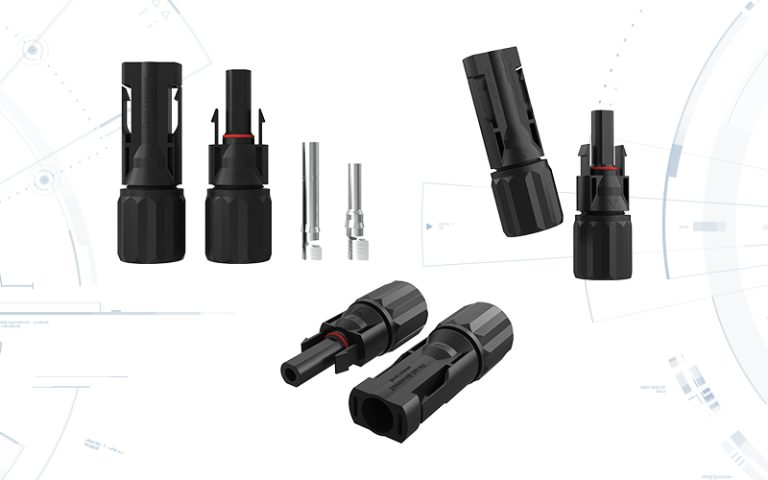
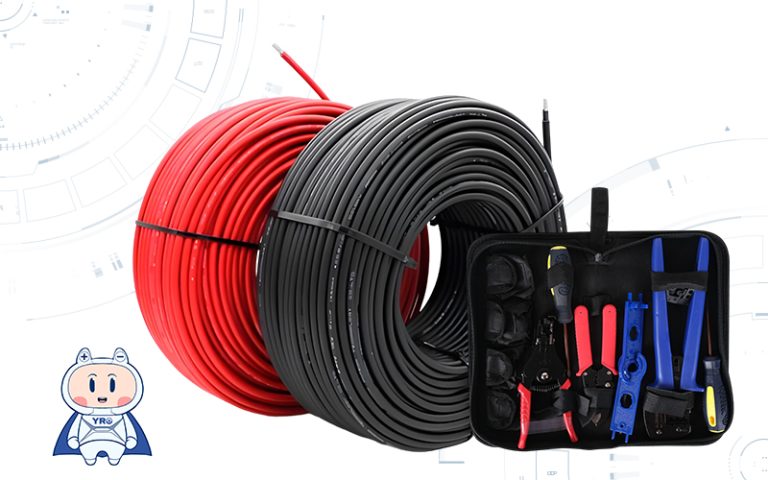
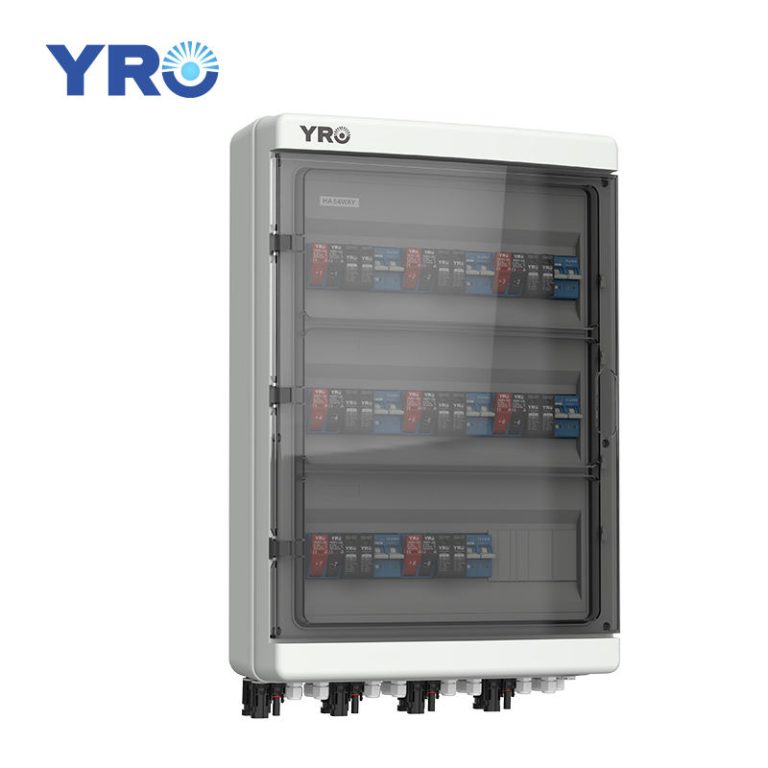
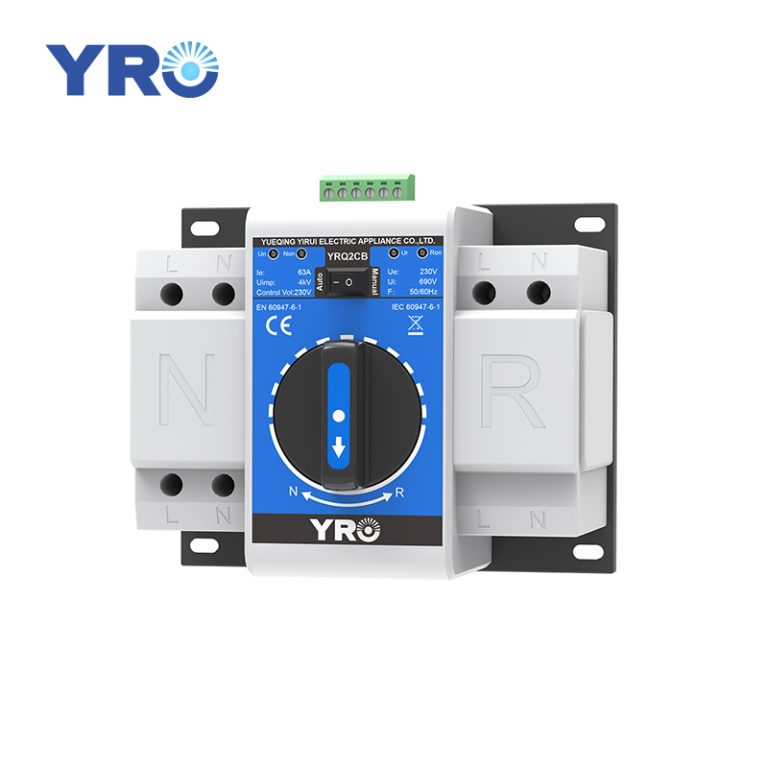
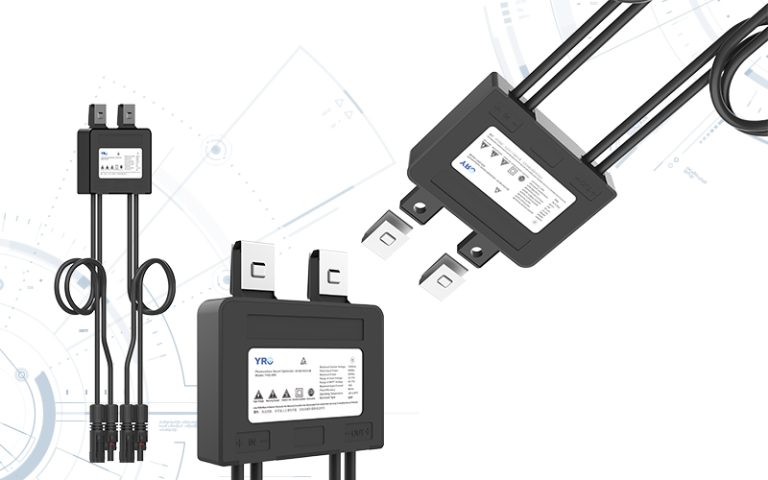
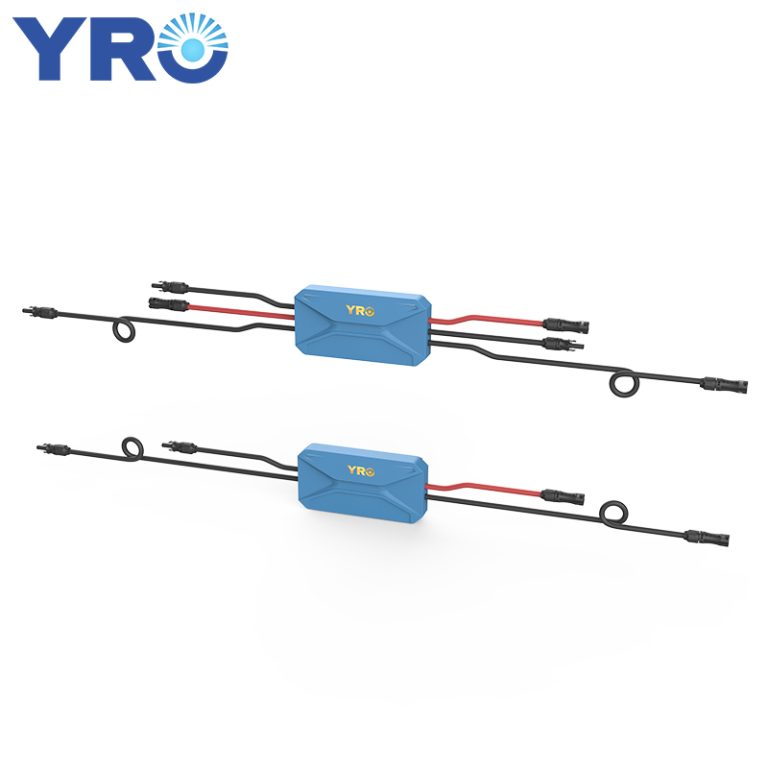
The combiner box plays a crucial role in photovoltaic (PV) solar systems, serving the primary purpose of combining the output from multiple solar panels or strings of panels into a single electrical output. Here’s a more detailed explanation of its purpose and function:
Combining Solar Panel Outputs: In a solar PV system, you typically have multiple solar panels installed on rooftops or in arrays. These panels generate direct current (DC) electricity from sunlight. A combiner box is used to gather the DC outputs from these panels.
Minimizing Wiring Complexity: Instead of running individual wires from each solar panel to the inverter (the device that converts DC power to usable AC power), a combiner box simplifies the wiring by consolidating these connections. This reduces wiring complexity and the risk of electrical faults.
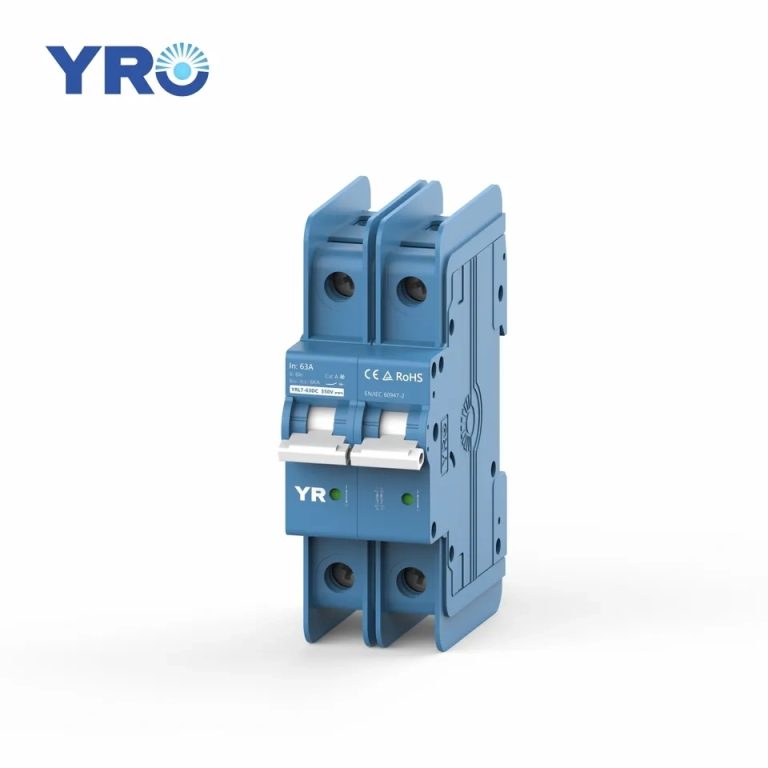
Overcurrent Protection: Combiner boxes are equipped with fuses or circuit breakers for each input string of solar panels. These protective devices are essential for preventing overcurrent situations, such as short circuits or excessive current flow, which could damage the panels or the electrical system.
Monitoring and Safety: Some combiner boxes include monitoring features to track the performance of individual strings of solar panels. Additionally, they often have safety features like disconnect switches, allowing maintenance personnel to isolate the PV array from the rest of the system when needed.
Compliance with Electrical Codes: Combiner boxes are designed to meet electrical code requirements and safety standards, ensuring that the PV system operates safely and reliably.
In summary, a combiner box is a critical component in solar PV systems that streamlines the electrical connections from multiple solar panels, provides overcurrent protection, enhances safety, and simplifies maintenance and monitoring of the system. It plays a vital role in ensuring the efficient and safe operation of solar power generation systems.

How many materials are in the converter box?

The number of materials in a converter box can vary depending on its design and purpose. Converter boxes are typically used for various applications, such as power conversion, signal conversion, or data conversion. The materials used in a converter box may include:
Casing/Enclosure: Usually made of metal or plastic, it houses the internal components and provides protection.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB): This is the main electronic component where various electronic parts are mounted.
Electronic Components: These can include capacitors, resistors, diodes, transistors, integrated circuits (ICs), and other electronic parts required for the specific function of the converter.
Wiring and Connectors: Various wires, cables, and connectors are used to interconnect the components and connect the converter box to external devices.
Power Supply Components: These components may include transformers, voltage regulators, and power capacitors, depending on the power requirements of the converter.
Cooling Elements: Some converter boxes may have heatsinks, fans, or other cooling elements to dissipate heat generated during operation.
Indicator Lights or Displays: Depending on the converter’s design, it may have LED indicator lights or displays to show its status.
Insulating Materials: These are used to prevent electrical contact between components and ensure safety.
Mounting Hardware: Screws, nuts, and other hardware for assembling and securing the converter box.
Labels and Markings: Information labels or markings that provide specifications, ratings, and safety instructions.
Please note that the exact materials and components in a converter box can vary widely based on its intended use and design. If you have a specific converter box in mind or need more detailed information, please provide additional details, and I’ll be happy to assist further.